Table Of Contents
Short Selling Meaning
Short selling refers to the trading activity whereby traders decide to sell stocks even before they buy them, given their high current market prices, which are expected to fall in the future. Traders and investors opt for these techniques for gains when the market turns bearish. This activity, however, is recommended for experienced market players rather than the amateurs.
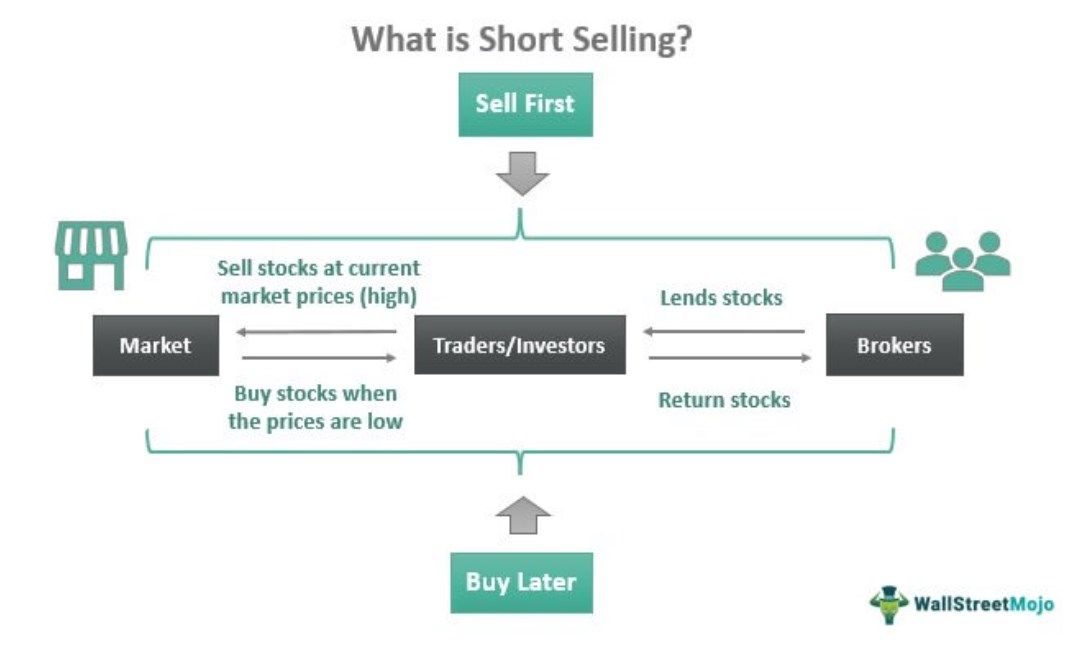
In the process, people borrow securities from brokers to sell them for profits when the prices are high and buy them in the same quantity at a later stage when the prices go low. Short selling is done either for gains when the prices are speculated to go low or to avoid risks of incurring losses due to the fluctuating market scenario.
Key Takeaways
- Short selling is a trading activity that occurs when investors expect the stock prices to go down after a significant increase.
- The traders, in this case, sell stocks first by borrowing the required volume of securities from available brokers and buy them later to return to the lender.
- A trader can sell a stock or an asset even if he does not own it in his portfolio.
- Investors short sell under two circumstances – speculation (when they aim at making profits by selling at higher prices and buying at a lower cost) and hedging (when they wish to avoid expected future risks).
Short Selling Explained
A short selling strategy, in simple terms, involves selling first and buying later. Though it is hard to believe that traders trade in stocks they don't even own, ace players widely adopt short sale strategies for profits or for hedging risks.
In short selling, investors borrow stocks, speculating future price drops, and sell them to interested buyers at high market prices. They buy the shares later at lower costs and return the stocks to the brokers they borrowed them from. The difference between the selling and buying prices becomes the profit for the investors.
Traders opt for short sale strategies under speculation, which indicate the possible risks associated with a market. On the other hand, portfolio managers adopt this trading technique to hedge risks by squaring off a position to avoid future risk exposure.
It is a risky investment strategy recommended for mature traders or experts. If the prices go down and the market turns bearish as expected, the stock borrowers make a profit. However, if the market continues to be bullish and the prices keep rising, they have to bear huge losses by buying the stocks at higher rates to pay back the original brokers.
Usually, traders have the liberty to hold on to the stocks for short sales for as long as they wish. However, there are instances where the brokers want the borrowed stocks covered soon. In India, short selling is allowed on Margin Intraday Settlement (MIS) basis. According to this, investors need to settle the stocks borrowed within the trading hours of the same day they sell them.
Why To Short Sell?
Short selling a stock occurs under two circumstances:
#1 - Speculation
Investors predict the prices of the stocks in the market. They utilize different strategies and technical indicators to assess the market scenario. They predict if the prices will go up or down depending on the same. If the prices are speculated to go down, the investors sell the stocks first by borrowing them from a broker. Later on, they buy the same number of stocks and return them to lenders, enjoying gains in the form of the difference between the selling price (high) and the cost price (low) of the stocks.
However, if the speculation turns opposite, investors have to bear huge losses by initially selling at a high price and buying at even higher prices later on.
#2 - Hedging
Investors opt for short sales to avoid the risks of lowering prices. As soon as they sense an expected fall in prices, they sell the stocks first and buy them later on from those who lend them the securities for short sell.
Though the purpose of speculation and hedging are the same, the difference is in the investors' intentions behind carrying out short selling.
How to Short Sell?
For traders to participate in short selling, they need to have a margin account. Accordingly, the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA), the Federal Reserve, and the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) have set some rules for the traders to maintain a minimum balance in their margin accounts. This minimum balance is termed the maintenance margin.
If the account balance falls below the minimum, traders need to add funds. If traders fail to maintain the margin, brokers might sell the position. In addition, the investors and portfolio managers have to pay interest on the borrowed shares until the position is closed.
Here are the steps involved in the process:
- Investors borrow stocks from brokers for a small fee. The broker either provides the securities themselves or connects with other financial institutions.
- Once traders receive the number of stocks ordered from brokers, they sell them at the current market price, be it under speculation or to hedge risks.
- As soon as the stock prices drop, they buy back the shares at a lower cost. The difference between the selling price and cost price becomes their profit.
- In an opposite scenario, i.e., if the prices continue to rise and the brokers ask traders to return the borrowed stocks, they are bound to buy the shares at a higher rate, incurring losses.
- The traders return the stocks to the broker, whatever the case may be.
Chart
Let us look at the following GAIL Industries Limited price chart to understand the concept.

The above chart shows that a downtrend might be on the horizon in the stock price. Hence, individuals may consider taking advantage of the downside move by short selling the stock. The strategy would involve keeping a target at Rs. 130.30 while placing a stop-loss order at Rs. 134. The stop-loss is a crucial element of a trader’s risk management strategy because the individual may incur substantial losses if the stock price rises instead of falling.
If the trader sells the shares of the company at Rs. 133.30 by borrowing from their broker, the broker will wait for the price to drop further and then will repurchase the shares sold at a lower price (Rs. 130.3). The returns earned following the deduction of any commission or interest would be the trader’s gains.
Individuals can observe similar charts of other financial securities available on TradingView to enhance their knowledge of short selling.
Examples
Let us consider the following short selling examples to understand how the strategy works:
Example #1
Short selling crypto is one of the significant examples to cite. The crypto and traditional financial markets work in the same way as far as a short sell is concerned. Harriett plans to short sell one Bitcoin worth $10,000. Thus, she borrows it from a broker and sells it at the current market value.
As soon as the price drops to $7,000, she buys a Bitcoin at a lesser cost and returns it to the broker along with interest due. The difference between the selling price and the cost price of the Bitcoin ($10,000 - $7,000 = $3,000) becomes Harriett's profit. She has to pay the interest applicable for the crypto from what is left to her.
Example #2
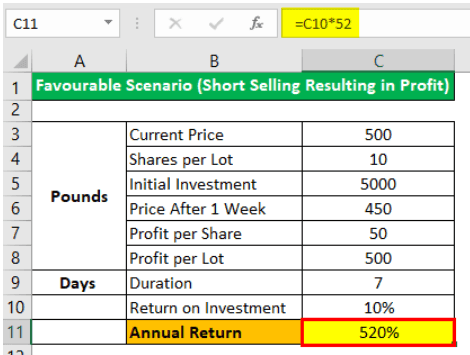
Consider a scenario where a stock is trading at $500. Though the quarterly results are to be released in a week, the competitor results indicated that the firm would post bad numbers.
A trader wants to utilize this opportunity and earn by short selling this stock. Since the trader does not own this stock, the person would have to borrow these stocks from his broker. After borrowing the stocks, the investor short sells the stock anticipating the stock price will go down. The plan is that the trader will buy back the stock once it has fallen by 10%.
Scenario 1
The quarterly results declared one week later are on expected lines, and the firm has posted a fall of 10% in profit every year. The stock prices crashed, and the stock declined by 15%. The trader seeks this opportunity and, maintaining financial discipline, closes his positions at $450, 10% down from the market price of the last week. The trader makes a profit of $50 (10%) on each lot. Assuming the contract was for ten lots, the person gains $500 on an investment of $5000.
The annual return would be:

Scenario 2
The above scenario was favorable when the stock price moved in the anticipated direction, and the trader made an annualized return of 520%. No assets in the world can give that return. However, on the contrary, if the firm had posted good results, the stock price might have boomed, and the traders’ position would have worsened. The results are summarized below.
The annual return would be:

Risks
When it comes to short selling, even the expert traders get poorly trapped in the deals, given the risks involved. Some of the risks that investors and traders must be aware of are as follows:
#1 - Regulatory Restrictions
The market regulators enjoy the right to allow or disallow short selling. As a result, the investors can never be sure of having the liberty to short sell their stocks. In the United States, regulators like the Securities and Exchange Commission can impose restrictions on the trading activities whenever necessary. They have the right to decide and enforce a ban on short sales to ensure the stock market does not collapse due to the sudden wide and wild price fluctuations.
#2 - Bad Timing
Time plays an important factor in the process. First, investors must be accurate enough in determining the point from which the stock prices are likely to fall. Then, there is a proper time to sell and buy the securities in the short sale. This is why it is considered a trading activity for mature and expert traders rather than amateurs or beginners.
#3 - Involves Borrowing
As the sale of stocks, in this case, occurs first, the investors need to have stocks in hand to fulfill buyers' requirements. Thus, they borrow shares from brokers, who might have to connect with larger market players to make them available to investors. The brokers become stock lenders in the process, and the traders need to return the stocks sooner or later.
If the prices go down, the investors profit by buying back those stocks at a lower rate. But, on the contrary, if the prices are up, the investors have to buy back the stocks at a higher price, incurring huge losses, to pay back the stock lenders.
#4 - More Expensive
It is more expensive than traditional trading activities. This is because the traders, in this case, are liable to pay interest based on the volume of stocks they borrow. They pay a portion of the profit investors to make as interest.
#5 - Short Squeeze
This instance occurs when short sellers get an opportunity to repurchase the stocks before the stock prices increase anymore. This way, the traders can ensure making losses as low as possible, given the continuous rise in the value of the stocks. A short squeeze helps traders when short selling backfires. However, such a phenomenon may lead to an increase in the prices for short sellers.
Pros and Cons
Short selling has its own set of advantages and disadvantages. Let us have a quick look at them:
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| High profits expected | Unlimited losses |
| Helps in hedging risks | More expensive |
| Reduces portfolio volatility | Short squeezes |
| Ensures risk-adjusted returns | Hard to borrow |
| Possibility of leveraged investments |